Serverless Architecture Set to Redefine Business Computing

Serverless is a highly trending term in the world of software architecture right now and one can judge this from the many references of the term in journals, products, and open source frameworks, with even a webinar dedicated solely to the subject. Through this blog post, we shall learn about the basics of Serverless and why it is so worth considering after all. So, let’s get started!
What is Serverless Architecture
So, what exactly do we mean when we use the term ‘serverless application’? Well, the term is used to refer to applications that, to a great extent, rely on third-party services (referred to as Backend as a Service or “BaaS”) or on a custom code that is run in ephemeral containers (Functions as a Service or “FaaS”). AWS Lambda is the most popular vendor host of FaaS. The basic fact underlying serverless computing is the fact that it allows you to build and run applications and services without having to think about servers. In other words, with serverless applications, you are not at all required to provision, scale, and manage any servers. Sounds pretty convenient, isn’t it? What’s more, you can build serverless applications for virtually any type of application or backend service, and everything that is otherwise required for running and scaling the application with high availability, is already taken care of for you!
How Serverless Architecture is Different
So, is a serverless application ‘serverless’ in the true sense of the term? Well, not quite, because they do have server hardware and server processes running for them after all! The only fact that differentiates it from the traditional approach, is that the organization that builds and supports a serverless application does not look after the hardware or the processes and these are outsourced to a third-party vendor instead! This way, the organization doesn’t need to invest in purchasing, renting, or provisioning servers or virtual machines for application development. Faas offers developers the platform for the execution of code in response to events without having to build and maintain the infrastructure. AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Microsoft Azure Functions, are a few renowned FaaS vendors.
Microservices to FaaS:
Serverless code that is created using FaaS complements code written using traditional methods, and both can be used in conjunction. Microservices is one such example of a traditional architecture and it involves breaking down of monolithic applications into smaller services for independent development, management and scaling. However, FaaS is one step ahead as it breaks down applications to the level of functions and events.
Diagram: A typical framework of an AWS serverless architecture
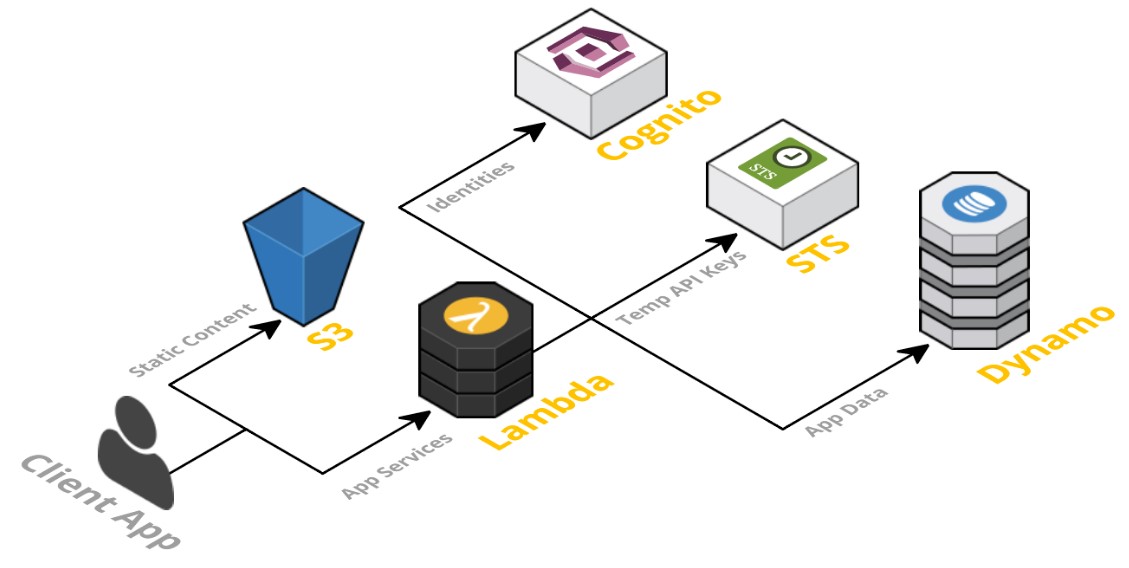
Image Source: http://blog.tonyfendall.com/
Web/Client Application is your application UI. It is best rendered in Javascript as you get a web server that is simple and static.
In FaaS, there is the concept of the ‘API Gateway’. A fully managed service, it is designed to make it simple for developers to publish, maintain, monitor and secure APIs at any given scale. Creating an API is easy through a few clicks on the Management Console and applications can use the API as a “front door” for the access to your back-end services for data, functionality, business logic and more.
Here we see that the application is supported by AWS Lambda, in which applications run on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2). The tasks involved in accepting and processing the innumerable concurrent API calls are all handled by the Amazon API Gateway, including authorization and access control, traffic management, monitoring, API version management, and more.
AWS Cognito is an identity service with AWS Lambda integration. There are several similar services available and their purpose is to provide User Authentication. AWS Cognito allows you to add sign-up and sign-in details of the users to your web and mobile applications. It also provides you the additional feature to authenticate your users through social media platforms, including Facebook, Twitter, and Amazon; and this can be accomplished through SAML identity solutions or through your very own identity system, if you have one. A fully managed NoSQL Database – such as DynamoDB – is essential for a serverless application.
The biggest threat caused by serverless applications is to the concept of containerization, which provides an open platform and developers find it easy to use the platform to push code from development to production. Some examples of containerization tools are Mesos, Kubernetes, and Docker, to name a few.
Benefits of Serverless Architecture:
Now let’s come to the advantages of serverless applications. To begin with, serverless applications allow your developers the time and energy to focus on the core product at hand, instead of having to worry about management and operation of servers or runtimes, be it in the cloud or on premises. This can go a long way in reducing overhead costs, and at the same time result in the development of better products that are of higher quality and are scalable. Here are the many benefits at a glance.
Operational Management made Easy
The serverless platform makes operational management easy and cost-effective through automatic scaling functionality offered by tools such as FaaS. The clear division between the applications and the supporting infrastructure, leads to higher quality products.
No Need for Server Management
The organization developing the application doesn’t have to worry about the provision and maintenance of servers, thus allowing the focus to improving the product. Also, there isn’t any requirements for installation, maintenance or administration of software.
Flexibility of Scaling
Serverless applications allow for easy scaling as they can be scaled automatically or by toggling throughput, memory and other units of consumption. This is in contrast with the complexity associated with scaling units of individual servers in a traditional application.
Built-in Default Capabilities
Another advantage associated with serverless applications is that the availability and fault tolerance capabilities are built into the system by default, unlike traditional applications that require you to architect for these capabilities.
Low Costs due to Zero Idle Capacity
Serverless applications help you cut down costs as you don’t pay when your code is not running. In other words, it rules out the requirement for pre- and over-provision capacity for storage, computation and the likes. No idle capacity translates to low costs.
So, we see that serverless architecture does have many benefits over the traditional approach.
Innovation is a key aspect of T/DG, and we continuously strive to serve our customers with the latest technologies and trends. It’s been now more than 5 years and we have successful case studies on projects like virtualization and private cloud. This has helped our developers to gain computing resources in a one-click step and now we are moving towards another transformation of automation for making application development a hassle-free process for the organization.
Learn more about our Services and Solutions in the www.thedigitalgroup.com/services/managed-infrastructure/ space. To schedule a meeting or for more information, please write to us at info@thedigitalgroup.com
