What is Cloud Computing? Things you Need to Know About the Cloud, Explained
Cloud computing received significant attention recently as it changes the way computation and services to customers. Cloud computing not only brings new business opportunities but also causes some major impacts on software testing and maintenance. Cloud computing is a means of using the Internet and remote servers for software applications, data access, data management and storage resources. Cloud computing allows consumers and businesses to use applications without installing software or accessing local files on their computers and hence can be used on any computer with Internet access. Users access cloud computing using networked client devices, such as desktop, computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones and any Ethernet enabled device such as Home Automation Gadgets.

img source:Brainpulley.com
Cloud Testing:
Cloud Testing is a means of testing cloud-based applications that use resources found in the cloud. By resources, we mean any element (hardware, software and infrastructure) necessary to carry out the tests. Cloud testing provides an end-to-end solution that transforms the way testing is done and can help an organization boost its competitiveness by reducing the cost of testing without negatively impacting mission-critical production applications. By leveraging a cloud computing solution for testing, organizations can shorten provisioning time because the cloud enables provisioning of test servers on demand. This helps ensure unused servers are not sitting idle.
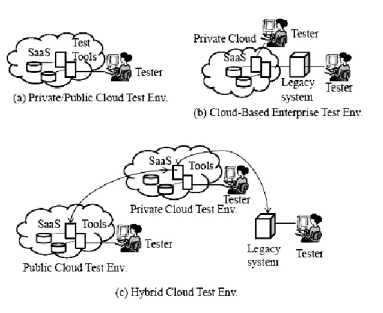
Three Types of Cloud Test Environments:
- A cloud-based enterprise test environment, in which application vendors deploy web-based applications in a cloud to validate their quality in a cloud infrastructure.
- A private/public cloud test environment, in which vendors deploy SaaS applications SaaS in a private (or public) cloud to validate their quality.
- A hybrid cloud test environment, in which vendors deploy cloud-based applications on a hybrid cloud infrastructure to check their quality.
source: 123innovations.com
Community Cloud:
Community cloud shares infrastructure between several organizations from a specific community with common concerns (security, compliance, jurisdiction, etc.), whether managed internally or by a third-party, and either hosted internally or externally. The costs are spread over fewer users than a public cloud (but more than a private cloud), so only some of the cost savings potential of cloud computing are realized.
What is Cloud Backup:
Cloud backup, or cloud computer backup, refers to backing up data to a remote, cloud-based server. As a form of cloud storage, cloud backup data is stored in an accessible from multiple distributed and connected resources that comprise a cloud.
How to Restore a Cloud Backup:
To update or restore a cloud backup, customers need to use the service provider's specific client application or a Web browser interface. Files and data can be automatically saved to the cloud backup service on a regular, scheduled basis, or the information can be automatically backed up anytime changes are made.
Cloud Computing Pros:
- Location independent access: The use of thin clients or virtualization significantly reduces hardware requirements, making it possible to test the services anywhere.
- Reduced cost of ownership: Using service provided by existing Cloud deployments removes the need to install and support hardware. The use of Cloud solutions makes it possible to centralize all IT components. Any maintenance steps will need to be executed only once, centrally, and they will be mirrored on all end user instances.
- Green IT: The reduced requirement for hardware, implementations and location dependence enables businesses to reduce the carbon footprint of its IT infrastructure.
- Productivity: It may be increased when multiple users can work on the same data simultaneously, rather than waiting for it to be saved and emailed.
- Reliability: It improves with the use of multiple redundant sites, which makes well-designed cloud computing suitable for business continuity and disaster recovery.
- Latest version availability: When you edit a document at home, that edited version is what you see when you access the document at work. The cloud always hosts the latest version of your documents.
- Requires a constant Internet connection: Cloud computing is impossible if you cannot connect to the Internet. A dead Internet connection means no work and in areas where Internet connections are few or inherently unreliable, this could be a deal-breaker
- Features might be limited: This situation is bound to change, but today many web-based applications simply are not as full-featured as their desktop-based applications. For example, you can do a lot more with Microsoft PowerPoint than with Google Presentation's web-based offering
- Stored data can be lost: Theoretically, data stored in the cloud is safe, replicated across multiple machines. But on the off chance that your data goes missing, you have no physical or local backup.
