Understanding the Types & Characteristics of Big Data

We all have heard the term ‘Big Data’ and Big Data is one of the most significant terms in the current times. Data experts say that enterprises today need to leverage the power of Big Data in order to gain the competitive edge and make informed decisions. Now, before we go ahead and learn about the multiple aspects of Big Data and the many types of Big Data, it is important to understand the significance of Big Data and what makes it one of the most powerful driving forces behind the success of the new age enterprise.

Types of Big Data
Big Data can be complex but to simplify things a little, we shall look at the 3 key types of Big Data as given below.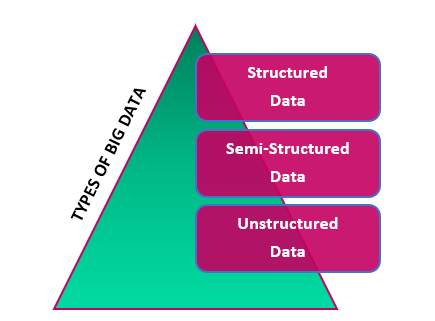
The first one among the many types of Big Data is structured data. It is any data that can be stored, accessed, and processed in a predetermined format. Over time, computer science has become more successful in inventing strategies for working with such structured data, when the format is fully understood in advance, and extracting valuable insights from it. Among the 3 types of Big Data, structured data is the easiest to analyze.
Examples
- Credit card numbers
- Dates
- Names
- Social Security numbers
- Zip Codes
- Airline reservation systems
- Sales transactions
2] Semi-Structured Data
Next in the list of the types of Big Data comes semi-structured data, which consists of structured as well as unstructured data. Semi-structured data appears to be structured in appearance, but it is not. Since most semi-structured data appears to be unstructured at first look, the distinction between unstructured and semi-structured data has always been blurred. Semi-structured data is information that is not in the standard database format as structured data, but has some properties that make it easier to process.
Examples
- XML, CSV & JSON documents
- Electronic data interchange (EDI)
- Portable Document Files (PDF)
- NoSQL databases
- HTML
- RDF
3] Unstructured Data
The third among the types of Big Data is unstructured data has no apparent format. Unstructured Big Data accounts for around 80% of the total volume of Big Data. Unstructured data is also further classified into machine-generated and human-generated categories based on its source. Machine-generated data accounts for all the satellite images, the scientific data from various experiments and radar data captured by various facets of technology. Human-generated unstructured data is what comes from mobile data, social media, and websites.
Examples
- Geo-spatial data
- Weather data
- Emails & messages
- Invoices
- Data from smart devices & IoT
- Analytics data
Characteristic Features of Big Data
Now that we have looked into what Big Data implies, let us move towards the characteristics of Big Data. Interestingly, the characteristics of Big Data were initially defined by the 3 Vs – Volume, Variety and Velocity. In addition to the 3 Vs, there is now also the 4th V which stands for Value.
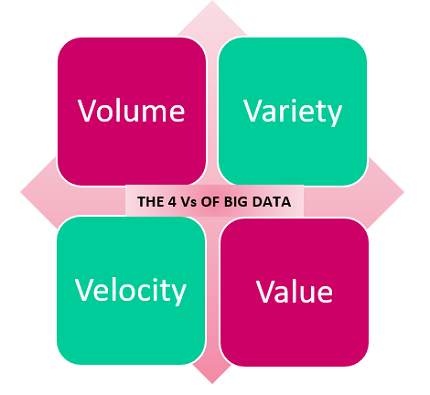
When it comes to Big Data, the name itself gives us an idea of what to expect when it comes to the volume. Big Data is enormous and to add to that, it is expanding at an explosive rate every minute, even as you’re reading this blog. Today, there are so many sources that generate data, such as smart devices, social media, smartphones, emails, online content, feeds, podcasts, videos, images, the list simply goes on and on. It is the sheer volume that defines Big Data, making ‘volume’ as one of the key characteristics to consider.
2] Variety
As we have seen earlier, Big Data consists of multiple sources of data and also consists of unstructured, semi-structured and structured data. To add to that, there are multiple sources of Big Data, including multiple formats like images, audio files, multimedia, PDFs, and so much more. This factor of variety is what makes it so much challenging for enterprises to analyze, store and maintain Big Data.
3] Velocity
Velocity is speed and it is one of the characteristic features of Big Data, as it is multiplying at a breakneck speed, as every millisecond, millions of bytes of data are being added. The purpose of Big Data analytics tools is to overcome the challenges in data processing and analysis that are caused by the enormous velocity of Big Data. The new age enterprise search platforms are an example.
4] Value
Value is another well-recognized attribute of Big Data because the most significant thing about Big Data is the amount of valuable insights that it holds within. The very purpose of making efforts to understand and analyze Big Data, in spite of the enormous volume and unstructured nature, is to extract the key insights for business decision making and growth. This makes Big Data extremely valuable when businesses need to make informed decisions that help them gain the competitive edge in the market.
So, with that we have covered the types and characteristics of Big Data, along with its significance. If you own a business today, you need to leverage the potential of Big Data in order to get access to the most relevant insights. To implement that, you need a new age advanced text mining tool like 3RDi Search – an enterprise search platform equipped with every text mining capability your enterprise needs to unravel insights from the most complex unstructured data.
