A Brief Introduction to Semantic Similarity
.png)
The computation of similarity between phrases, sentences, or texts that have the same meaning but are not lexicographically comparable is known as textual semantic similarity measurement. This is a significant issue in a variety of computer-related domains, such as data mining, information retrieval, and natural language processing with new age enterprise search tools.
Wikipedia defines Semantic Similarity as "A concept whereby a set of documents or terms within term lists are assigned a metric based on the likeness of their meaning/semantic content."
It evaluates the shared semantic evidences derived from one or more knowledge sources (e.g., textual corpus, thesaurus, taxonomies/ontologies, etc.) to estimate the taxonomic likeness of two terms.
For example, sofa and couch are similar because they are both pieces of furniture with a similar purpose.
What is Meant by Similar Entities?
Semantic similarity, also known as "semantic closeness/proximity/nearness," is a notion in which a metric is assigned to a set of documents or terms within a term list based on the similarity of their meaning/semantic content. It is one of the key features of an enterprise search platform like 3RDi Search.
Two entities can be termed as similar under one of the following conditions:
- Both belong to the same class
- Both belong to classes that have a common parent class
- One entity belongs to a class that is a parent class to which the other entity belongs
Two relationships can be termed as similar under one of the following conditions:
- Both belong to the same class
- Both belong to classes with a common parent class
- One relation belongs to a class that is a parent class to which the other relation belongs
Here are a few different algorithms used to measure semantic similarity between words, and is important to know in the context of the new age enterprise search platforms like 3RDi Search.
1]Path Length Score
Path Length is a score that represents the number of edges that connect two words in the shortest path. In a thesaurus hierarchy graph, the shorter the path between two words/senses, the more related they are.

This score includes log smoothing and it indicates the number of edges between two words/senses. This is similar to path length with log smoothing and has the same features, except that due to the log smoothing, it is continuous in nature.

3] Wu & Palmer Score
This is a score that considers the positions of concepts c1 and c2 in the taxonomy in relation to the Least Common Subsumer (c1, c2). In path-based measurements, it considers that the similarity between two concepts is a function of path length and depth.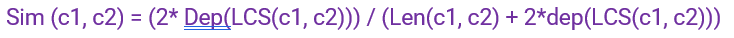
Based on the Information Content (IC) of the Least Common Subsumer, this score indicates how similar two-word senses are.
The frequency counts of concepts contained in a corpus of text is displayed as information content. Each time a concept is observed, the frequency associated with the idea is updated in WordNet, as are the counts of the ancestor concepts in the WordNet hierarchy (for nouns and verbs).
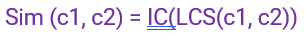
This is a number that takes into account both the amount of information required to state the similarities between the two concepts as well as the amount of information required to fully describe these terms.
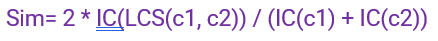
Semantic similarity is a significant concept today as it has multiple applications in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and forms one of the building blocks of the new age enterprise search platforms. Want to witness semantic similarity through our 3RDi Search platform? Visit www.3rdisearch.com or drop us an email on info@3rdisearch.com and our team will get in touch with you.
